
Cash plays a vital role in every financial plan, as it helps us cover day-to-day expenditure, and meet short-term liabilities. Without cash, we would be unable to pay bills and everyday essentials, and instead we would need to realise other assets – which may well carry an opportunity cost – or use debt. Holding a cash reserve also provides peace of mind that any unexpected expenditure, such as repairing the car or fixing the boiler, can be met.
Whilst holding a cash reserve is the foundation of a sound financial plan, holding too much cash can have adverse consequences and lead to erosion of wealth over time. With interest rates starting to fall, we feel it is a good time to review existing cash savings to see if they could be better employed.
How much cash is too much?
The “correct” balance of cash held by an individual is undoubtedly a personal preference. Holding cash provides a feeling a security, and as we are all different in terms of our tolerance of investment risk, the most appropriate balance we hold in cash will differ. A general starting point would be to aim for a cash buffer of around six months’ worth of household outgoings; however, many prefer to hold a larger balance depending on the mix of other assets they hold, and in particular if assets are illiquid, such as residential property.
It may also be appropriate to hold a higher balance in cash if funds are required in the short-term, as investing funds with a brief time horizon increases the level of risk. For example, you may hold a higher cash balance temporarily for a specific purchase, such as a property, or to make a gift to a relative.
Hidden risks
Many believe cash savings to be risk free, and whilst the balance in a savings account does not fluctuate in value, hidden risks can damage your wealth over time. Inflation reduces the purchasing power of cash and is a factor that some do not consider. If the inflation rate is higher than the interest earned on cash (which is often the case) the real value of your cash diminishes.
The chart below demonstrates the eroding effects of inflation, by comparing the compound returns achieved by cash (represented by the Bank of England Base Rate – blue) compared to the increase in prices generally (represented by the UK Consumer Price Index – red) over the last 10 years. As you can see, returns on cash have not kept up with prices, and even achieving cash returns in excess of the Bank of England Base Rate (illustrated by the Bank of England Base Rate +1% in green) would still lead to erosion.
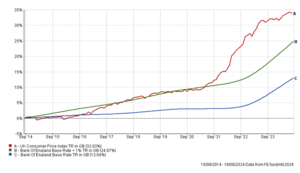
We have recently been through a period when the Bank of England Base Rate exceeds the rate of increase in the Consumer Price Index, and therefore the best cash accounts have provided savers with positive real returns. The current position is, however, something of an anomaly, and given that we expect base interest rates to fall further, we are likely to see a return to negative real returns on cash deposit.
Why keeping a cash balance is important
It is sensible planning to keep a proportion of your overall wealth as cash. One of the key roles that cash can play in a diversified investment strategy is that it can provide a buffer zone, which can allow longer-term investments to stay in place during periods when market conditions disappoint. For example, if you regularly withdraw funds from an investment portfolio, or a pension account in Flexi-Access Drawdown, holding a cash buffer can provide the ability to suspend withdrawals at a time when investment markets are weak, allowing time for the investments to recover before restarting regular withdrawals again.
Maintaining a cash balance can also provide the opportunity of adding to an existing investment portfolio, if markets dip. Finally, holding a small proportion of an investment account in cash can mean that platform and adviser fees are covered by the cash balance, and avoids the need to sell assets to cover ongoing portfolio costs.
Missed opportunities
Holding excessive cash means missing out on potential investment returns that can be achieved from other assets that are able to generate superior returns over time, which can lead to substantial financial underperformance.
Historically, returns achieved from equities, bonds and commercial property have outperformed cash. The annual Barclays Equity-Gilt study has analysed the returns from various asset classes since 1899, and when considering returns from 1899-2022, their evidence shows that over an investment period of two years, the probability of equities outperforming cash is 70%. Looking at longer-term performance, over an investment period of 10 years, the probability of equities outperforming cash increases to 91%.
One reason for the outperformance is that returns from equities are derived from two sources – the prospect of capital growth over the longer term as the value of the investment increases, together with income in the form of dividends. Equities also act as a hedge against inflation, as a company’s revenue and earnings should, in theory, rise in line with inflation over time.
The Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) have issued a warning over excessive allocations to cash held in workplace and private pensions. Given the likelihood of underperformance over the longer term, the FCA are concerned that those holding significant cash balances over an extended period of time risk a poor outcome. New rules came into force late last year that require pension providers to send cash warning letters to customers holding more than 25% of their pension fund in cash for more than six months.
Reallocating surplus cash
Given the eroding effects of inflation, holding surplus cash deposits is likely to damage your financial wealth over the longer term. That said, if you have limited experience of investment in other asset classes, moving funds away from the perceived safety of cash can be a little daunting.
This is where the benefit of speaking to an independent adviser can prove invaluable. At FAS, our experienced advisers can provide guidance and reassurance and ensure that investments are well-diversified into a range of different asset classes, with the mix of assets tailored to your financial requirements, and attitude to risk. Speak to one of our holistic advisers to discuss the level of cash that you hold and consider alternative investment options.





